Benchmarking Super DCA Against Leading DCA Platforms: A Comparative Analysis
Introduction
Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA) is a popular investment strategy, and its on-chain implementation is pivotal for decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. The Super DCA protocol offers a unique approach to DCA with its Time-Weighted Average Market Maker (TWAMM) model, leveraging advanced integrations with Superfluid, Uniswap, and Gelato. This post presents a comparative benchmarking study of Super DCA against Mean Finance and Sushiswap, focusing on performance, investment patterns, and value accrual mechanisms.
Benchmark Overview
Parameters:
- Initial Balance: 100 USDC per platform.
- Duration: 30 days.
- Metrics Evaluated: Net Asset Value (NAV) performance, USDC and ETH holdings over time.
Platforms Benchmarked:
- Super DCA (Experimental TWAMM)
- Mean Finance
- Sushiswap
Results and Analysis
Net Asset Value (NAV) Performance Over Time
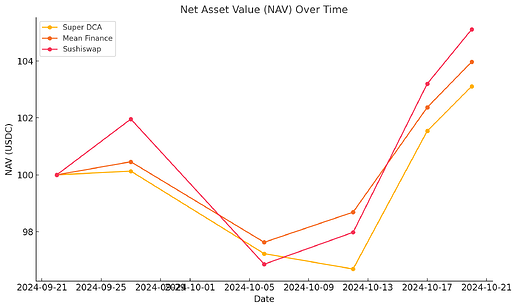
The NAV performance showcases the ability of each platform to generate returns while accounting for execution fees. Figure 1 illustrates the NAV growth trends:
- Super DCA acheived a +3.11% NAV gain by the end of the benchmark period.
- Mean Finance consistently grows, finishing with a +3.97% NAV gain.
- Sushiswap, has a minimum order of 50 USDC so it executed 2 trades in the 30-day trial, leads with a +5.11% NAV gain which is biased by the performance of the price of Ethereum
Figure 1: NAV Performance Over Time
Percentage Performance Comparison
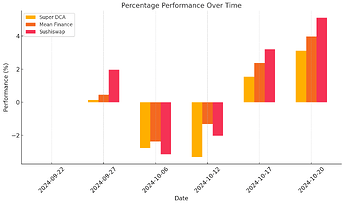
Figure 2 shows the percentage performance for each method over time:
- Super DCA’s Liquidity Network is low liquidity and the dynamic fee is not responsive enough to high gas prices, when the price of ETH fell the gas prices were elevated and degraded the performance of Super DCA.
- Mean Finance offers steady, incremental gains.
- Sushiswap’s large early investments result in higher returns earlier in the cycle and results in the best performance, though strongly biased by the experimental set up and market price action.
Figure 2: Percentage Performance Comparison
[Included in follow up post due to a limit on the media that can be added in one post]
USDC and ETH Holdings Trends
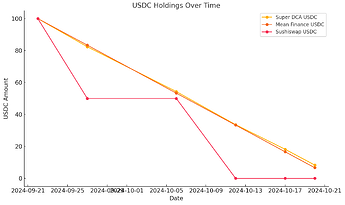
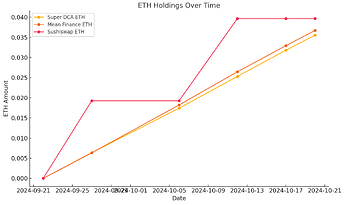
The contrasting investment strategies are evident in Figures 3 and 4:
-
USDC Holdings (Figure 3):
- Super DCA and Mean Finance steadily reduce USDC balances, reflecting incremental investments.
- Sushiswap depletes USDC rapidly in two large transactions early in the benchmark period.
-
ETH Holdings (Figure 4):
- Super DCA and Mean Finance gradually accumulate ETH through consistent DCA.
- Sushiswap shows larger ETH acquisitions corresponding to its bulk purchases.
Figure 3: USDC Holdings Over Time
[Included in follow up post due to a limit on the media that can be added in one post]
Figure 4: ETH Holdings Over Time
[Included in follow up post due to a limit on the media that can be added in one post]
Data
The data from the benchmarking activity can be found in this Google Sheet and contains the address of the wallets used for benchmarking: Super DCA Benchmarks - Google Sheets
Key Takeaways
Observed the Super DCA Effect in Production
At times the Super DCA system did reach close to and better than the theoretical 0.11 lower bound fee. This is mostly attributed to the Super DCA system at times getting prices that are better than the oracle price. This is a side-effect of the construction of the Super DCA Liquidity Network.
Dynamic Fees Impact Performance
Super DCA’s innovative fee structure dynamically adjusts based on trading volume, aligning with its TWAMM design. This results in a dip during low-volume, high-gas price phases but showcases robust recovery with high-volume, low-gas price phases. This is a design flaw and future versions should improve the responsiveness of the dynamic fee. It should charge higher fees in situations where the gas is high and a swap has not executed for a while. The current system stalls when gas prices quickly move up and the result is a large swap with high slippage ends up occurring when gas prices subside.
Investment Strategies Differ
Sushiswap’s large, fewer trades achieve higher short-term gains but may not align with the principles of dollar-cost averaging. It had a high minimum swap limit of 50 USDC per swap. This makes it hard for the kind of person looking to buy the average price over a month with a budget of < 50-100 USDC. Super DCA and Mean Finance exemplify incremental investment patterns since they use a similar method for quantizing orders into small periodic swaps.
Future Steps
- Expand benchmarks to longer periods and diverse market conditions.
- Optimize Super DCA’s dynamic fee mechanism for greater efficiency.
- Simplify user interfaces and staking mechanisms to enhance adoption.
Join the Conversation!
We invite the community to provide feedback, share insights, and discuss the implications of these results for token engineering and DeFi innovation.
Thank you for your support!
This is a research project that has been very hard to fund. Thanks to TEC, I have been able to get this project onchain, and it has now been collecting several months of activity data.
Regards,
Mike Ghen (@mikeghen)